Why in News?
The 17th G20 summit concluded recently with the adoption of Bali declaration.
More on News
• The motto for this G-20 summit was Recover Together, Recover Stronger.
• Also, India took over the presidency of G20 from Indonesia.
Key Highlights of the Bali Declaration-2022
• The Group highlighted its differences in the on-going war in Ukraine and asked for Russia’s complete withdrawal from the territories of Ukraine.
• Group also reassured its Commitment to secure Global Food security.
o The Group welcomed the Black Sea Grain initiative brokered by Turkey and UN.
✓ It is an MoU signed between Russia and UN Secretariat to allow export from Russia and Ukraine on food products and fertilizers, to ease the tension in the region.
• The Group has welcomed the provision of additional financial resources, to assist in financing critical gaps in implementing International Health Regulations (2005)
o It also applauded the establishment of a new Financial Intermediary Fund for Pandemic PPR (the ‘Pandemic Fund’) hosted by the World Bank.
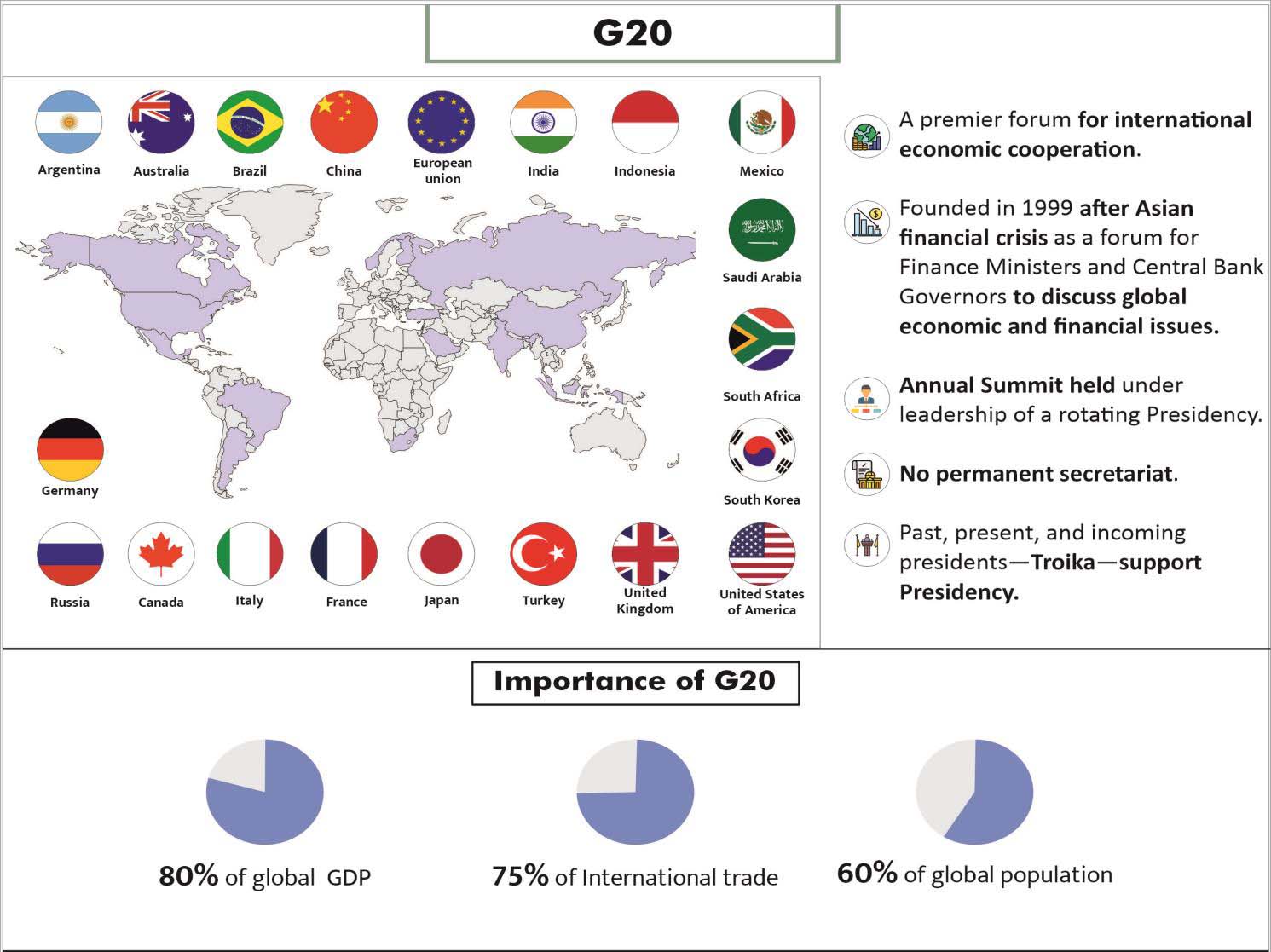
Significance of G20 in current Geopolitical situation
• Authority on major international economic issues
– The G20 plays an important role in shaping and strengthening global architecture and governance on international economic issues.
o It was particularly useful in steering the global economy after the global financing crisis and banking collapse of 2008.
o G20 has spearheaded reforms for international financial institutions such as reforms to the international tax system, through the G20/OECD Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project.
• Egalitarian grouping – it is an acceptable medium between the more elitist G-7, and the 38-member Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
o Over the past two decades, global economic balance has shifted, and G-20 has been seen as a more representative and egalitarian grouping of global leadership.
• Focus on low-income countries– It is a platform where leaders’ commit to working with developing countries, particularly low-income countries by providing policy coherence, analysis and practical tools to support growth and development.
o It recognizes that development and global economic issues cannot be tackled separately.
• Fulfilment of SDGs – achievements include measures to drive sustainable growth and enhance global stability; cooperation on tax transparency, lowering cost of remittances and increased female participation etc.
Challenges for G20
• Internal Governance Challenge – Though the group was intended to be more inclusive than G7, there is no formal membership criteria established still.
o The membership is based on a country’s systemic importance to global financial markets and its contribution to GDP and trade only.
o There is no inclusive membership for the least developed countries.
• No Code of Conduct established – There is a lack of a code of conduct for members and clear, enforceable rules that enable action against members if they breach any rules.
o The Group could have had a better say in the on-going Russia-Ukraine war, if such codes were established.
• Multilateral commitments on aid and trade are faltering – This is because the role of the United Nations and the World Trade Organization in securing cooperation between donor and recipient country groups is losing centrality.
o There are now three socio-economic systems — the G7, China-Russia, and India and the others — and they will jointly set the global agenda.
• Geopolitical tensions – Geopolitical tensions, spurred by strategic competition between China and the United States, have increasingly threatened cooperation within the group.
• Countries are turning to international lenders for bailouts – The G20 introduced a common framework for debt treatment ahead of its 2020 summit, but only three countries—Chad, Ethiopia, and Zambia—have requested debt relief under the framework.
o Others have gone towards organisations like IMF.
• Friction regarding climate change – China, India, Russia, and Saudi Arabia reportedly blocked an agreement on phasing out coal use and fossil fuel subsidies at a July 2021 meeting of environment ministers.
o Also, following the invasion of Ukraine, Germany and other G20 countries have reneged on previous promises to stop financing fossil fuel projects overseas.
Way forward
• Revised theoretical framework of macro and microeconomics – G20 members need to incorporate lessons from the recent crisis to advocate policy actions based on economic theory that needs revision.
• Avoiding Internal Fracturing – Collective action and problem solving should be encouraged that transcends traditionally like-minded groups of countries.
• Improving Outreach – The G20 must promote equitable international economic arrangements that provide a larger voice and role for the major economies of the global South.
o The G20 must also reach out to non-member states and non-state actors and give voice and consideration to their concerns.
• Establishing a code of Conduct for the members– by having an established code of conduct the Group can have a better say on controlling the acts of aggressive members like China and Russia.